A team of scientists comprised of Juergen Schieber, a Professor in the Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences within the College of Arts and Sciences at Indiana University Bloomington, and colleagues on NASA’s Curiosity Rover mission, uncovered the first tangible evidence for sustained wet-dry cycling on early Mars. The latter condition is considered essential for prebiotic chemical evolution, a stepping-stone towards the emergence of life.
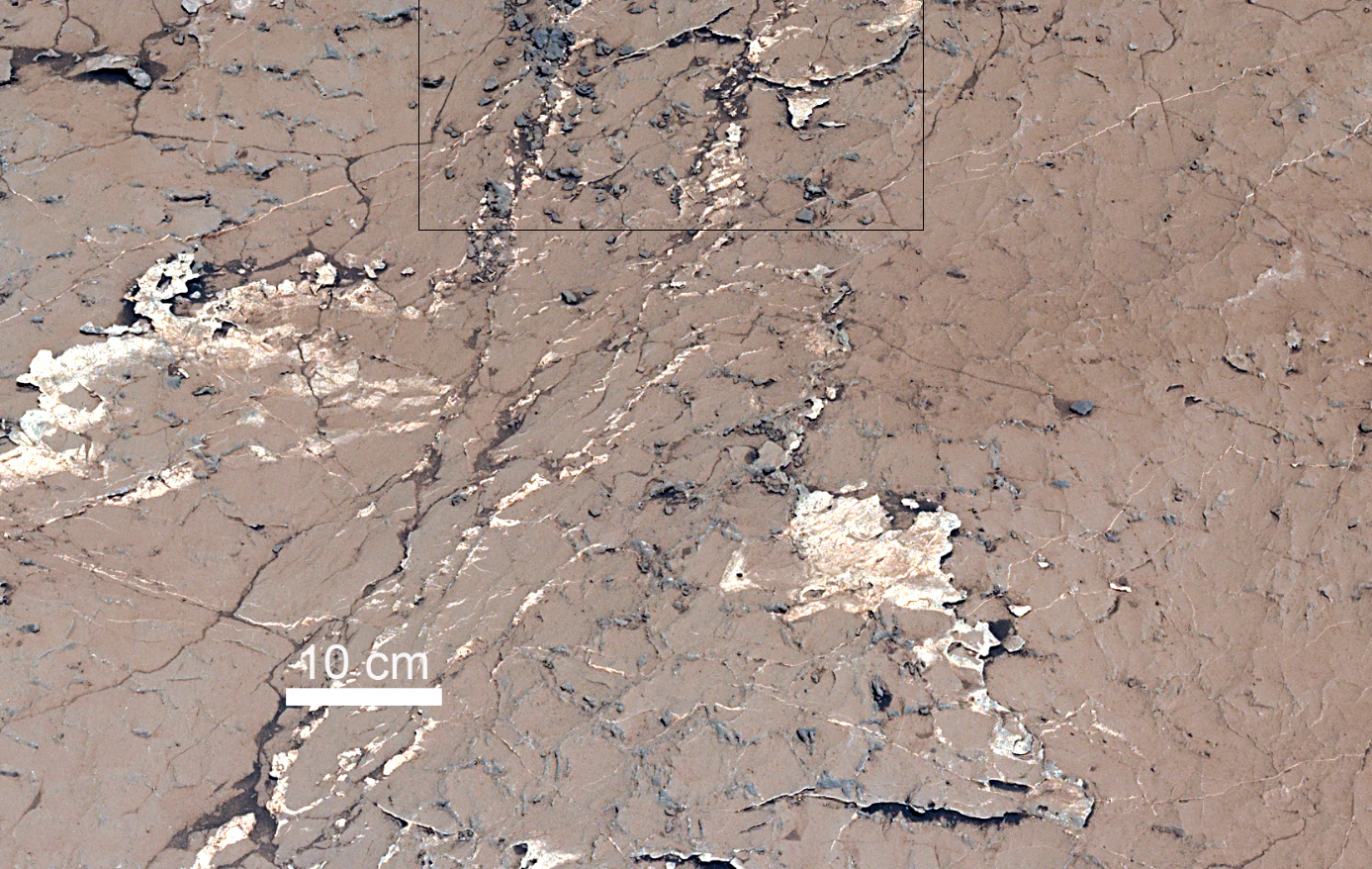
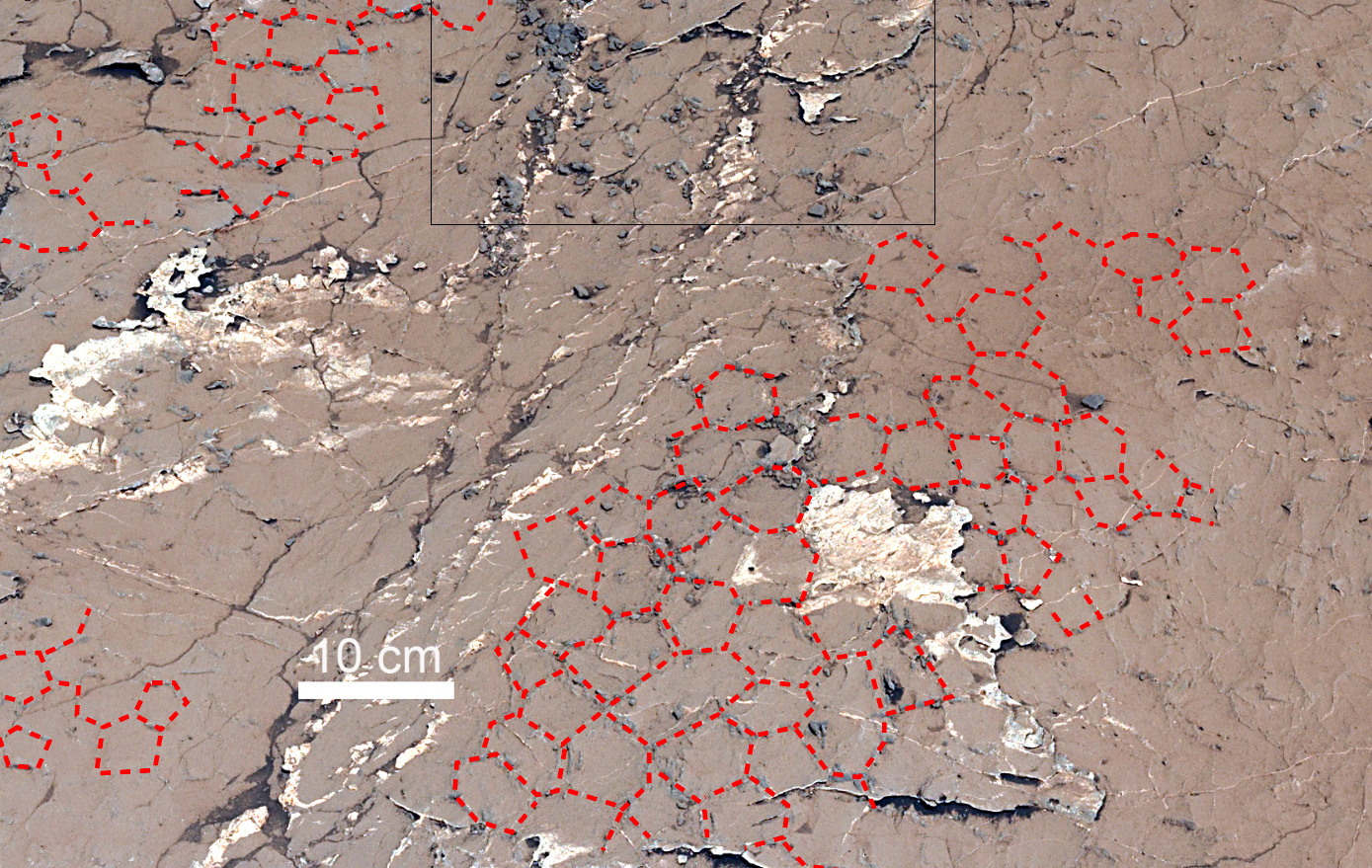
In a new paper, “Sustained wet-dry cycling on early Mars,” published in the scientific journal Nature, Schieber and his co-authors utilized data from the Curiosity Rover that currently explores Gale Crater to examine ancient pattern of mudcracks filled with salt (geometric patterns like pentagons or hexagons) observed in 3.6 billion year old mudstones. As mud dries out, it shrinks and fractures into T-shaped junctions – like what Curiosity discovered previously at “Old Soaker,” a collection of mud cracks lower down on Mount Sharp. Those junctions are evidence that Old Soaker’s mud formed and dried out once, while the recurring exposures to water that created the new mud cracks caused the T-junctions to soften and become Y-shaped, eventually forming a hexagonal pattern.
Although Professor Schieber’s main research interest is the geology of shales and mudstones on Earth, his interest in the underlying fundamentals prompted him to postulate an abundance of mudstones on Mars, and that got him into a conversation with people that were planning the Mars Science Lab (MSL) Curiosity Rover mission at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “Given my expertise about these rocks I was invited to join the MSL science team, and since landing in August 2012, 11 years ago almost to the day, our traverse has been dominated by mudstones,” said Professor Schieber.
Sustained wet-dry cycling on Mars—a consequence of a repeated desiccation, recharge, and flooding, creates cracks in the lake bed and within those cracks high salt concentrations develop that force the crystallization of minerals left after the lake’s evaporation, and cementation of sediment. Ultimately this process was preserved as the polygonal (hexagon- or pentagon-shaped) patterns observed with the Rover. Due to desiccation, the residual water likely had high concentrations of dissolved salts and, potentially, of organic molecules that can serve as the building blocks of life.